| Supported Targets | ESP32 | ESP32-C2 | ESP32-C3 | ESP32-C5 | ESP32-C6 | ESP32-C61 | ESP32-P4 | ESP32-S2 | ESP32-S3 |
| ----------------- | ----- | -------- | -------- | -------- | -------- | --------- | -------- | -------- | -------- |
# Encrypted Binary OTA
This example demonstrates OTA updates with pre-encrypted binary using `esp_encrypted_img` component's APIs and tool.
Pre-encrypted firmware binary must be hosted on OTA update server.
This firmware will be fetched and then decrypted on device before being flashed.
This allows firmware to remain `confidential` on the OTA update channel irrespective of underlying transport (e.g., non-TLS).
* **NOTE:** Pre-encrypted OTA is a completely different scheme from Flash Encryption. Pre-encrypted OTA helps in ensuring the confidentiality of the firmware on the network channel, whereas Flash Encryption is intended for encrypting the contents of the ESP32's off-chip flash memory.
> [!CAUTION]
> Using the Pre-encrypted Binary OTA provides confidentiality of the firmware, but it does not ensure authenticity of the firmware. For ensuring that the firmware is coming from trusted source, please consider enabling secure boot feature along with the Pre-encrypted binary OTA. Please refer to security guide in the ESP-IDF docs for more details.
## ESP Encrypted Image Abstraction Layer
This example uses `esp_encrypted_img` component hosted at [idf-extra-components/esp_encrypted_img](https://github.com/espressif/idf-extra-components/blob/master/esp_encrypted_img) and available though the [IDF component manager](https://components.espressif.com/component/espressif/esp_encrypted_img).
Please refer to its documentation [here](https://github.com/espressif/idf-extra-components/blob/master/esp_encrypted_img/README.md) for more details.
## How to use the example
This example can use either RSA or ECIES-P256 for pre-encrypted OTA. You must first select your desired scheme:
1. Run `idf.py menuconfig`.
2. Navigate to `Component config` -> `Pre Encrypted OTA Configuration`.
3. Set `Pre-encrypted OTA Scheme` to your choice:
* `RSA-3072 encryption`
* `ECIES encryption`
4. If you selected `ECIES encryption` and will be using the HMAC-derived key, ensure `HMAC EFUSE KEY ID` is set to the eFuse block where `ecc_key/device_hmac_key.bin` will be burned.
5. Save the configuration and exit.
Once the scheme is selected, follow the relevant sub-section below for key generation and specific setup.
### Creating RSA key for encryption
You can generate a public and private RSA key pair using the `esp_enc_img_gen.py` tool or `openssl`.
Using `esp_enc_img_gen.py`:
```bash
python esp_enc_img_gen.py --generate_rsa_key
```
This will create `rsa_pub_key.pem` and `rsa_priv_key.pem` in the current directory.
Using `openssl`:
`openssl genrsa -out rsa_key/private.pem 3072`
This generates a 3072-bit RSA key pair, and writes them to a file.
Private key is required for decryption process and is used as input to the `esp_encrypted_img` component. Private key can either be embedded into the firmware or stored in NVS.
Encrypted image generation tool will derive public key (from private key) and use it for encryption purpose.
* **NOTE:** We highly recommend the use of flash encryption or NVS encryption to protect the RSA Private Key on the device.
* **NOTE:** RSA key provided in the example is for demonstration purpose only. We recommend to create a new key for production applications.
### Steps for ECIES Scheme
To test the ECIES-based encryption scheme:
1. **Configure for ECIES** (Ensure `ECIES encryption` is selected in `menuconfig` as described above):
* Run `idf.py menuconfig` (if not already done, or to verify).
* Navigate to `Component config` -> `Pre Encrypted OTA Configuration`.
* Select `ECIES encryption` for the `Pre-encrypted OTA Scheme`.
* Set the `HMAC EFUSE KEY ID` to the eFuse block number (0-5) where you will burn the `ecc_key/device_hmac_key.bin`. The default is -1 (disabled), so this must be changed.
* Save the configuration and exit.
2. **Key Management**:
* This example provides a pre-generated HMAC key and its corresponding public key in the `ecc_key/` directory (relative to this example).
* `ecc_key/device_hmac_key.bin`: The HMAC key that needs to be burned into the device\'s eFuse.
* `ecc_key/public.pem`: The device public key, derived from `device_hmac_key.bin`. This key will be used by the build system to encrypt the firmware.
* **Burn the HMAC Key to eFuse**:
Use the `idf.py efuse-burn-key` command to burn the `ecc_key/device_hmac_key.bin` to the eFuse block you configured in `menuconfig`.
For example, if you set `HMAC EFUSE KEY ID` to 0:
```bash
idf.py efuse-burn-key BLOCK_KEY0 ecc_key/device_hmac_key.bin HMAC_UP
```
Replace `BLOCK_KEY0` with the correct eFuse block if you chose a different ID (e.g., `BLOCK_KEY1` for ID 1).
* **(Alternative) Generate New Keys**: If you prefer not to use the provided keys, you can generate a new set:
```bash
python <path_to_esp_encrypted_img>/tools/esp_enc_img_gen.py --generate_ecc_key
```
This will create `device_hmac_key.bin` and `device_pub_key.pem` in the current directory. You would then need to:
1. Replace `ecc_key/device_hmac_key.bin` and `ecc_key/public.pem` with these new files (or update the example to point to them).
2. Burn the new `device_hmac_key.bin` to the eFuse.
3. **Build, Flash, and OTA**:
* Follow the steps in "Build and Flash example" and "Configure and start python based HTTPS Server" below. The build system will use the ECIES scheme and the public key (e.g., `ecc_key/public.pem`) to generate `build/pre_encrypted_ota_secure.bin`.
* **NOTE:** The keys in the `ecc_key/` directory are for demonstration purposes only. We recommend creating a new key pair for production applications.
## Build and Flash example
```
idf.py build flash
```
* An encrypted image is automatically generated by build system. Upload the generated encrypted image (`build/pre_encrypted_ota_secure.bin`) to a server for performing OTA update.
### Configure and start python based HTTPS Server
After a successful build, we need to create a self-signed certificate and run a simple HTTPS server as follows:
* Create server_certs directory, Navigate to server_certs directory `cd server_certs`.
* To create a new self-signed certificate and key, run the command `openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout ca_key.pem -out ca_cert.pem -days 365 -nodes`.
* When prompted for the `Common Name (CN)`, enter the name of the server that the "ESP-Dev-Board" will connect to. When running this example from a development machine, this is probably the IP address. The HTTPS client will check that the `CN` matches the address given in the HTTPS URL.
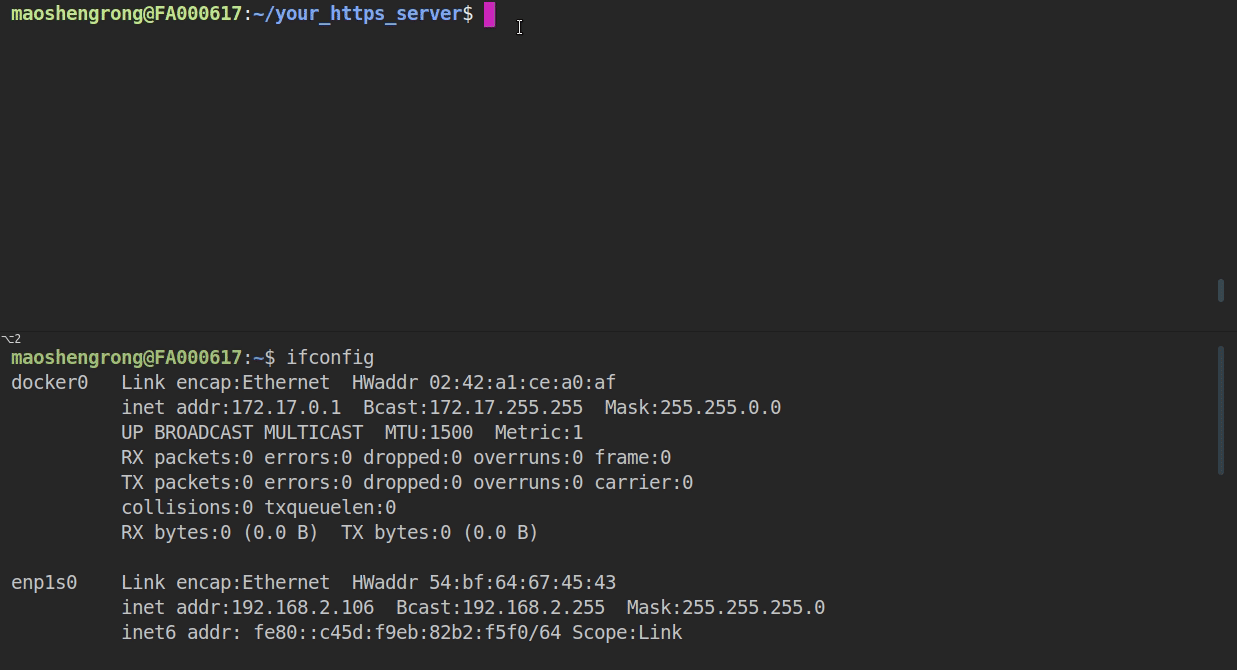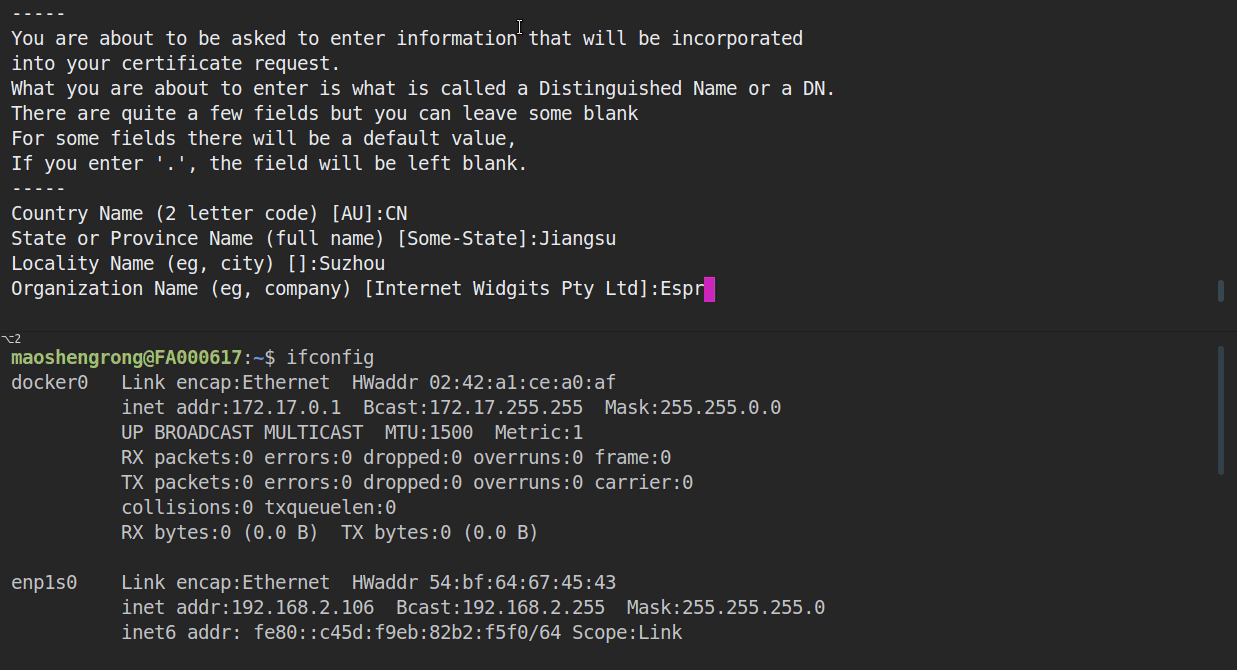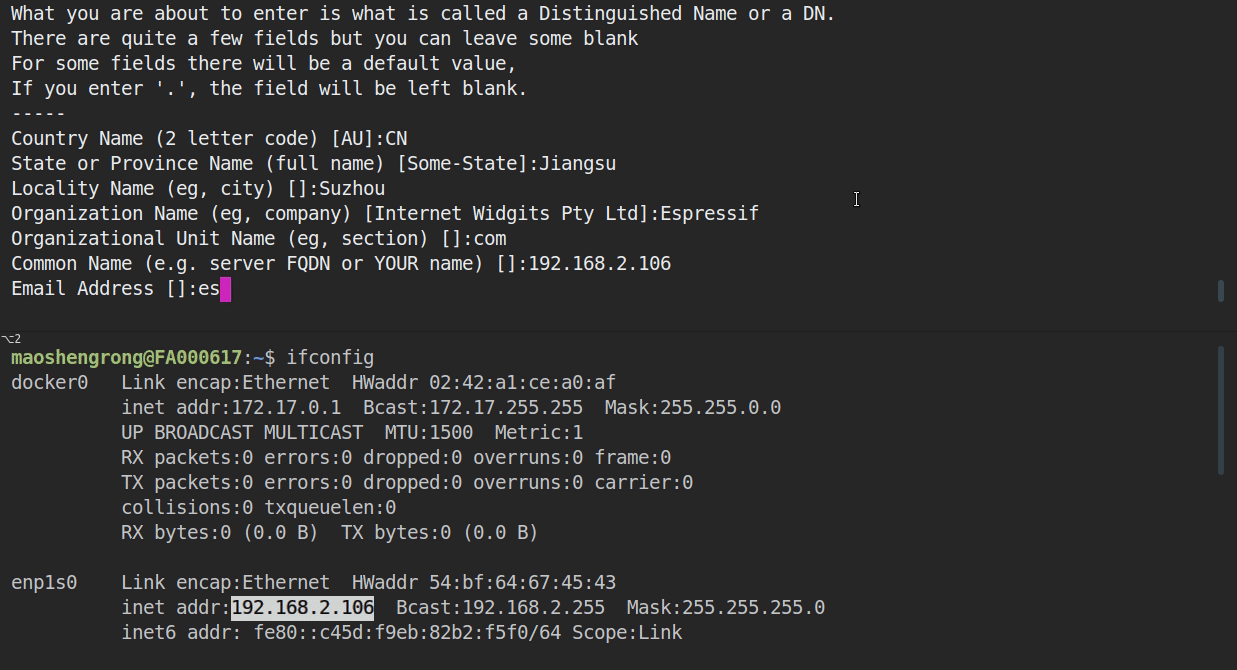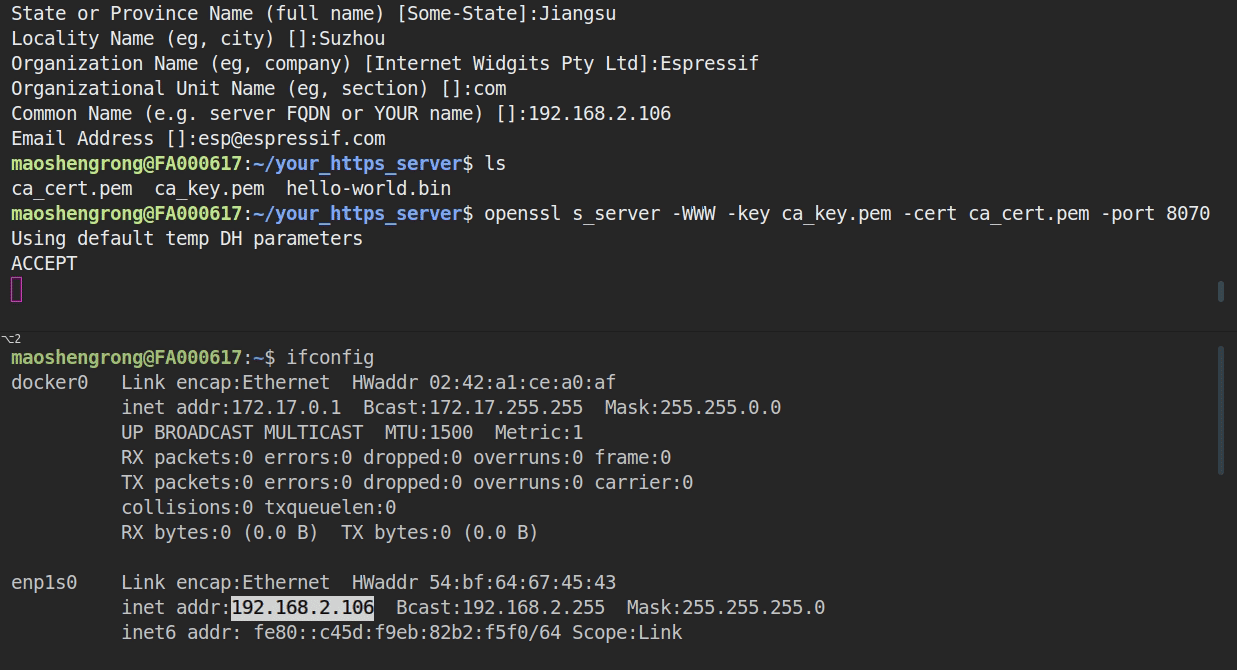
You can start the server using following instructions:
After the successful build, start the local python based HTTPS server using the certificate and key present in the 'server_certs' directory (certificate: ca_cert.pem and key: ca_key.pem).
To start the server use the following command -
```
python pytest_pre_encrypted_ota.py build 8070 server_certs
```
1. build - build directory (where the new firmware image is present) will be exposed
2. 8070 - server port (user can use any port)
3. server_certs - cert directory where the certificate and key is present (here same ca_cert.pem is used in main/pre_encrypted_ota.c and server_certs dir). If user wants to use own certificate and key just pass the directory name, in which the certificate and key is present.
* Note - If you don't want to create certificates then just run the `pytest_pre_encrypted_ota.py` without passing `server_certs` directory, the server will use the hardcoded certificates present in `pytest_pre_encrypted_ota.py`
## Configuration
Refer the README.md in the parent directory for the setup details.
To create a project from this example, run:
idf.py create-project-from-example "espressif/esp_encrypted_img=2.4.0:pre_encrypted_ota"